陳世勳

- 期刊論文
- 學經歷
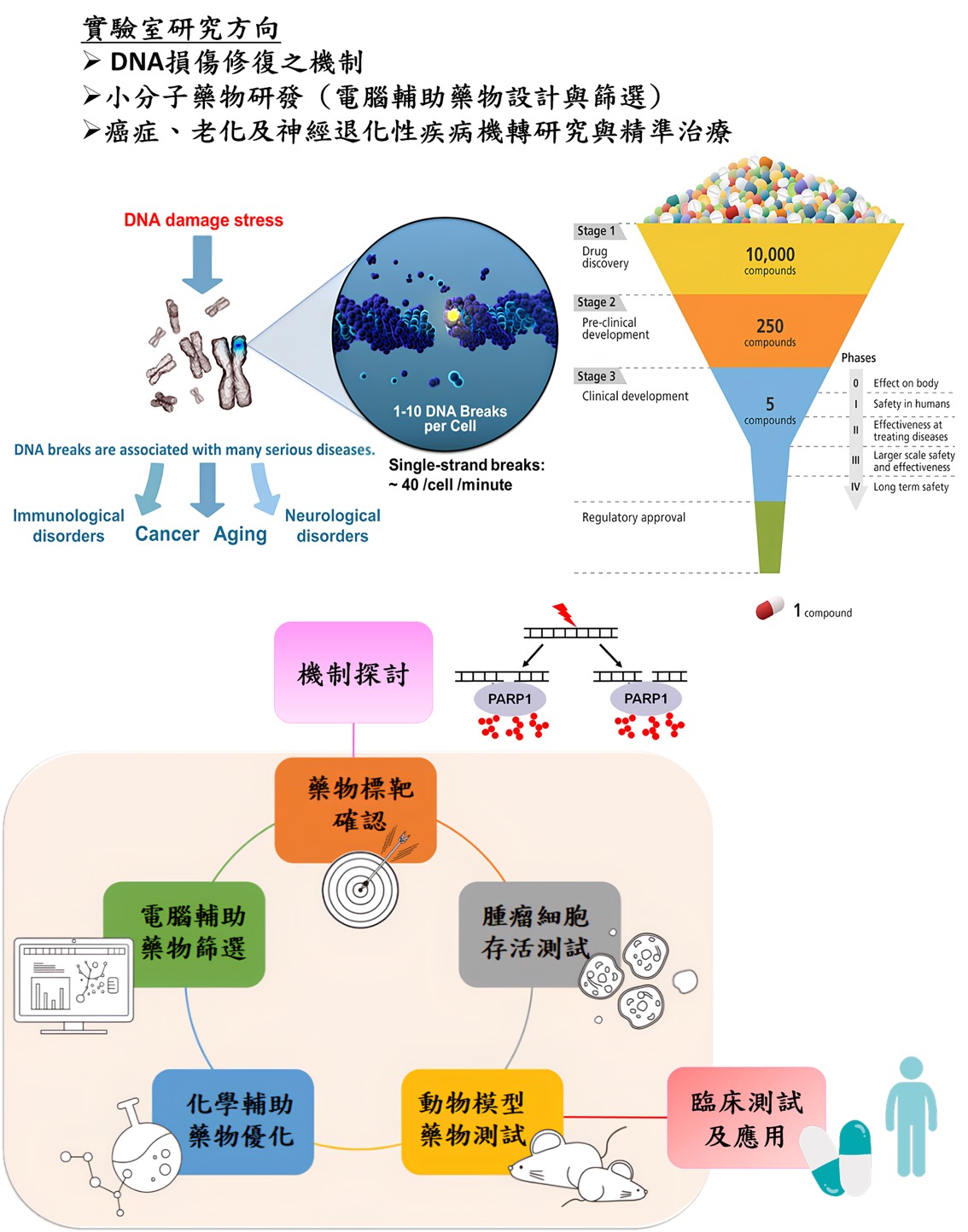
- 研究方向
- 學生榮譽事項 / 徵才
Research interests of our laboratory
Our research interests focus on exploring the mechanisms of DNA repair and treatments of DNA repair-related diseases (such as cancer, aging, neurodegenerative diseases, etc.) Based on mechanistic studies, we will identify small-molecule drugs or novel strategies for the treatments of human diseases. The topics are divided into four directions:
DNA repair is closely related to human diseases
DNA damage often occurs in the cells of every person's body. What causes DNA damage in our cells? There are two main sources, one is exogenous factors (such as radiation, viral infection, and chemicals), the other is endogenous stresses that are from replication errors and cellular metabolism (such as reactive oxygen species). Once DNA damage occurs, it will affect cell cycle, transcription, DNA repair, and cell apoptosis. Because lots of single-stranded and double-stranded DNA will break in each cell cycle, even in every minute, and DNA damage involves in some important biological processes, it is associated with many human diseases, such as immunological disorders, cancer, aging, and neurological disorders. Thus, DNA repair is very important when DNA damage occurs. DNA repair defects will cause gene instability and the occurrence of diseases (Figure 1).
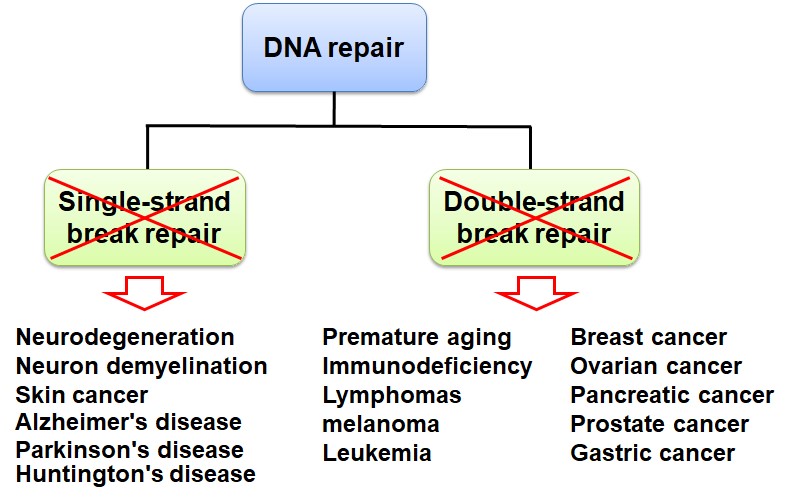
Figure 1. Loss of DNA repair causes many human diseases, including tumorigenesis, aging, neurodegenerative diseases etc.
Post-translational modifications are important for DNA repair
Post-translational modifications, such as protein phosphorylation, ADP-ribosylation, ubiquitination, acetylation, and methylation, are important for numerous biological processes, including DNA damage response. It has been reported that protein phosphorylation, ADP-ribosylation, and ubiquitination facilitate DNA single-strand break (SSB) and/or double-strand break (DSB) repair. Numerous studies investigating ADP-ribosylation have been performed in the last several decades. Yet, our understanding of the molecular mechanisms governing ADP-ribosylation signaling and the physiological and pathophysiological importance of the pathways regulated by ADP-ribosylation are still poorly understood. Thus, there are many exciting findings waiting to be discovered in this field of research. For example, the enzymatic activities of “ADP-ribosylation erasers” have been studied but their biological functions in DNA damage response are still unclear (Figure 2). Moreover, the relationship between ubiquitination, acetylation or methylation and DNA repair is also worth further investigating.
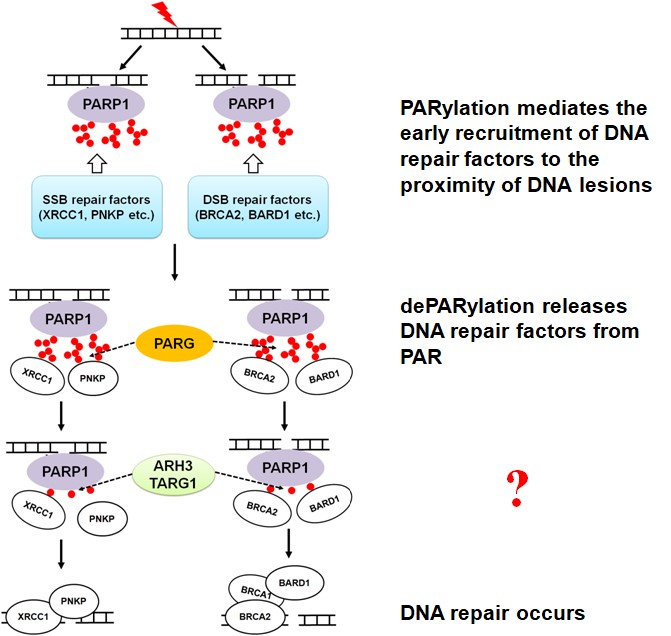
Figure 2. mono- and poly-ADP-ribosylation play an important role for DNA repair
Mechanism-based drug discovery for DNA repair-related human diseases
Our previous study shows that BRCA-deficient breast and ovarian cancer cells are hypersensitive to the treatment of PARG inhibitor, COH34 (Figure 3). Thus, similar to PARP and PARG inhibitor, small molecules that suppress DNA repair are able to be utilized for cancer chemotherapy. In particular, PARP inhibitor has been applied in the clinical treatment of cancers with BRCA mutation. Thus, we plan to examine if DNA repair-defective breast, ovarian, lung, colon, and pancreatic cancers are hypersensitive to these small molecules identified by our in silico strategies. In addition to cancer, DNA repair is also associated with aging and neurodegenerative diseases. The new drug targets and small-molecule regulators for anti-aging and neurodegenerative diseases will be identified based on mechanistic studies. We expect that our studies could be applied for clinical treatments in the future.
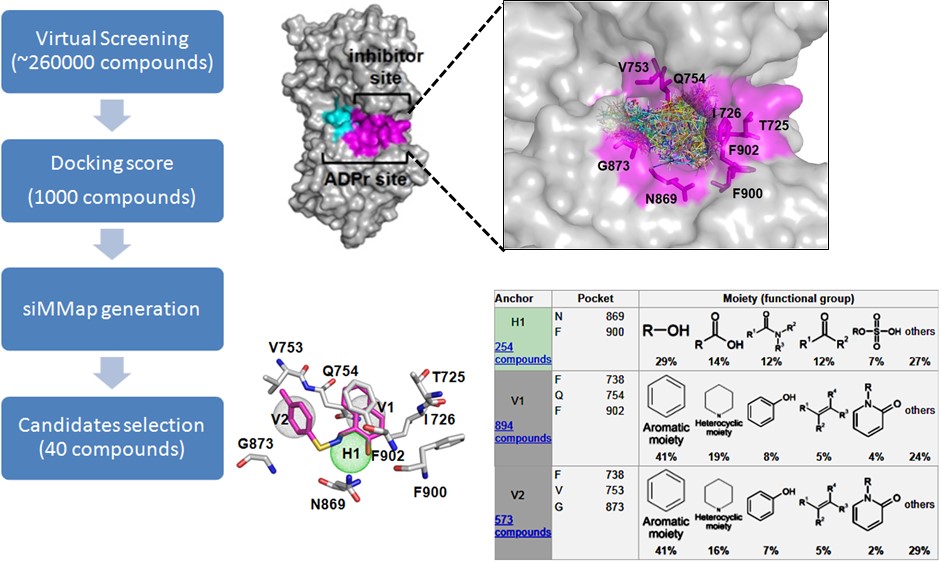

Figure 3. Using in silico strategy with siMMap analysis to identify novel PARG inhibitor (COH34) for DNA repair-defective cancer treatments.
1. 誠徵 專任研究助理 (學士或碩士級):
2. 誠徵 大學專題生:
(1) 大一 ~ 大四皆可
(2) 無經驗可,只要態度積極認真,願意學習,
(3) 能夠適應實驗室生活
3. 誠徵 實驗室工讀生:
(1) 大一 ~ 大四皆可
(2) 無經驗可,只要做事認真細心,有責任感
(3) 歡迎想先體驗看看實驗室環境的學生應徵
以上意者請提供 (工讀生除外)
1. 履歷表 (應徵助理者請列出至少一位推薦者姓名與連絡方式)
2. 未來規劃與應徵動機
3. 其他相關有利於審查之文件
請將上述資料e-mail 至 shichen@ntu.edu.tw 陳世勳老師,合適者將通知面談,名額額滿為止。
2022年
高英傑(大專生) 中研院x台大生化所暑期計劃 壁報暨口頭競賽 優勝
2023年
高英傑(大專生) 中研院x台大生化所暑期計劃 壁報暨口頭競
林宣宏(大專生) 中研院x台大生化所暑期計劃 壁報暨口頭
2024年
林姵玟(大專生) 中研院x台大生化所暑期計劃 壁報暨口頭競
林姵玟(大專生) 台大生化科學所碩士班推甄 正取
2025年
許璧蘭(碩士生) 第39屆聯合生醫年會壁報競賽 進入決選
高英傑(大專生) 美國華盛頓大學(UW)、南加州大學(USC)
